Overview
Business Model Generation (BMG) referred to as Business Model Canvas was developed by Alexander Osterwalder , Yves Pigneur and Alan Smith along with contribution from around 470 different business practitioner from around the globe (around 45 countries for specific).
It is a way of describing business in terms of: customers and their related activities, the value proposed by the business, the key supporting entities and basic financial analysis in a cost-benefit format.
It is very important for any business s to have a document that represents the business model and there are other ways to plan for the business like the Feasibility Study.
Business Model Canvas Building Blocks
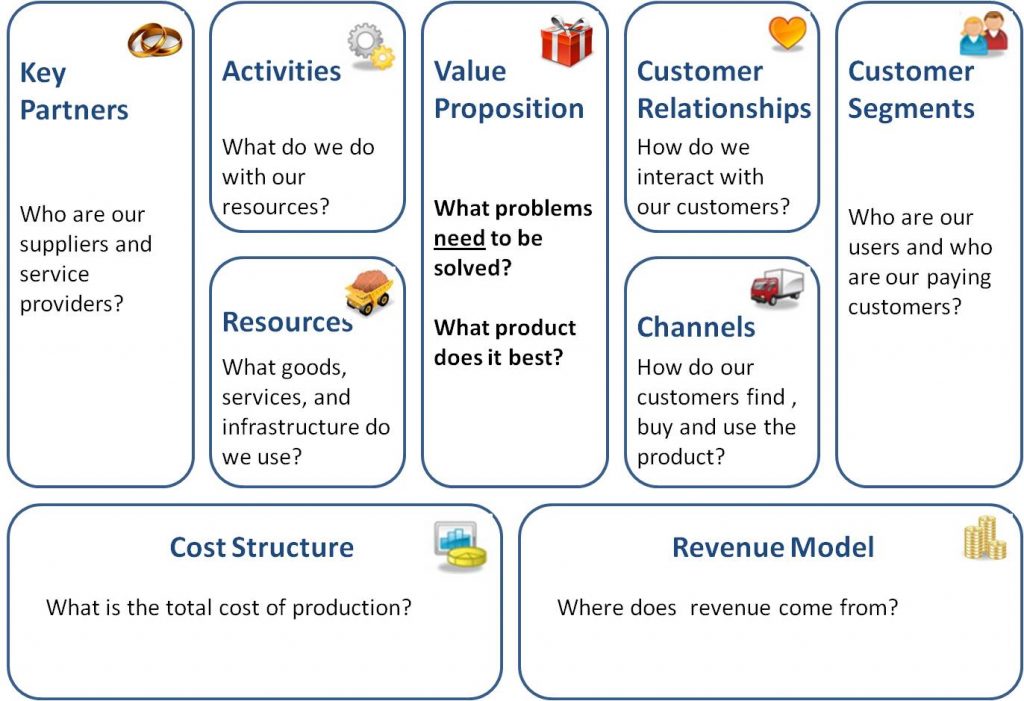
It consists of nine building blocks as follows:
- Key Partners.
- Key Activities.
- Key Resources.
- Value Proposition
- Customer Segmentation
- Customer Relationship
- Channels
- Cost Structure
- Revenue Streams
Why to use Business Model Canvas?
It can be used for more than one reason:
- Planning for business.
- Reviewing Current Business state
- Monitoring Business Performance
How To Prepare Business Model Canvas?
We will go through each building block together to provide further clarification regarding how to prepare a business model canvas.
Key Partners
the key partners are the legal entities/ companies / people who you count on doing your business.
They could be your main suppliers, sponsors or investors.
In some cases the key partners relation with the business can be extended to a more formal legal form lie acquisition or merging
why you should have key partners?
When you have key partners, you can reduce the business risk in their related issues.
for example if you have a main supplier who has a strong supply chain, it helps you to reduce the risk of getting short of stock.
Also having a key partner might be the answer if you have a specific shortage of a specific business capability; like recruitment process.
Key Resources
the key partners are the assets that you need to undertake your business operations.
And they are divided into Four types:
- Physical; like machines, branches or logistics.
- Financial; like the cash needed to run the day-to-day operations.
- Intellectual; like the patents required to start producing a specific product or a specific industry experience.
- Human: like when you need a specific SME (Subject Matter Expert) to help in a specific business operation; ex: you need a skilled hospitals architect to prepare the designs of a new hospital construction project.
Key Activities
the key activities are the main activities that are necessary to start, operate and run your business; including delivering your services, selling your products and making the required maintenance or activities to keep operating your firm or company.
Key activities can be classified as:
- Value-add: the main services or products manufacturing for which the clients are willing to pay (ex: might be doctor giving a consultation or a patient diagnosis) .
- Non-value-add: the other main activities that you do in order to run your business for which the clients are not willing to pay (ex: might be doctor’s clinic marketing activities, it is necessary for the business, however the clients are not willing to pay for it).
- Business non-value-add: activities that must be included in the products you well or the services you provide to meet regulatory and other needs for which the clients are not willing to pay (ex: might be doctor’s clinic book keeping, it is necessary for the business, however the clients are not willing to pay for it).
Value Proposition
A value proposition is what the client is willing to trade for getting their needs fulfilled or problem solved.
the proposition may be in a form of one or more services or products or a mixture of services and products that can fulfill the client requirements or solve their business issue.
Customer Segmentation
customer segmentation is grouping clients according to their common needs, or other attributes that can be geographical (location, ..) or typographical (age, gender, ..) so that the firm/company can address their common needs or similar problems more effectively with the right service or product.
the firm/company may consider different ways for client grouping (customer segmentation)
As an example based on:
•Different needs for each segment.
• Varying profitability between segments.
• Different distribution channels.
• Formation and maintenance of customer relationships.
Customer Relationship
Customer relationships can vary between formal to informal , general to personalized are categorized generally into:
Customer Acquisition
Customer Acquisition in the way the business acquire their clients from the market, which might be through different ways or channels as explained in the channels section through which the relationship can vary from a personal one between the salesman and the client or general one between the company’s website / portal and the client.
Customer Retention
Customer Retention is the ways the company keep their clients on a continuous sales process (up-selling and cross selling) making the client as productive in revenue generation as he can be.
Also this can be in different ways as mentioned in the customer acquisition section above.
What is most important is to decide what is the best way to handle the customer relationship in your company according to your business model.
Channels
Channels are the different ways an enterprise interacts with and delivers value to its customers. Some channels are very communication-oriented (for example, marketing channel), and some are delivery-oriented (for example, distribution channel). Other examples include sales channels and partnering channels.
Enterprises use channels to:
• raise awareness about their offerings,
• help customers evaluate the value proposition,
• allow customers to purchase a good or service,
• help the enterprise deliver on the value proposition, and • provide support.
Understanding channels involves identifying the processes, procedures, technologies, inputs, and outputs (and their current impact), as well as understanding the relationship of the various channels to the strategies of the organization.
Cost Structure
Every entity, product, or activity within an enterprise has an associated cost. Enterprises seek to reduce, minimize, or eliminate costs wherever possible. Reducing costs may increase the profitability of an organization and allow those funds to be used in other ways to create value for the organization and for customers. Therefore, it is important to understand the type of business models, the differences in the types of costs and their impact, and where the enterprise is focusing its efforts to reduce costs.
Revenues Streams
A revenue stream is a way or method by which revenue comes into an enterprise from each customer segment in exchange for the realization of a value proposition. There are two basic ways revenue is generated for an enterprise:
revenue resulting from a one-time purchase of a good or service and recurring revenue from periodic payments for a good, service, or ongoing support.
Some types of revenue streams include:
• Licensing or Subscription fees: the customer pays for the right to access a particular asset, either as a one-time fee or as a recurring cost.
• Transaction or Usage fees: the customer pays each time they use a good or service.
• Sales: the customer is granted ownership rights to a specific product.
• Lending, Renting, or Leasing: the customer has temporary rights to use an asset.
Drawbacks
There are some drawbacks of using business model canvas:
- It can not be used as a business plan; as it doesn’t describe a lot of details like the market analysis.
- It can not used be as a financial plan; as it is not considering any financial planing or analysis.
- It can not be used as a feasibility study; as it is not considering the business potential environment or profitability.
to conclude business model canvas is a very useful tool used for idea validation sometimes or basic business planning but you need to make sure why you are using it to make the best of it.
Feasibility Study
The feasibility study counts for the following:
- Business description.
- Market feasibility study.
- Technical feasibility study.
- Financial feasibility study.
- Organizational feasibility study.
- The conclusions.
Difference between Business model Canvas and Feasibility Study
there is a big difference between business model canvas and feasibility study where each one is used for a different purpose as explained above.


